Building Your First API: A Hands-on Guide with Python and Flask
Unlock the power of APIs with a simple and easy-to-follow tutorial on creating your own web service using Python and Flask
Hello Backend Developers,
In this edition of our newsletter, we'll take a hands-on approach and guide you on how to create your first API using Python. Before diving into the code, let's first understand what is an API and how it works.
What is an API?
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols that allow different systems to communicate with each other. It is a way for different software systems to interact with each other, share data and functionality, and automate tasks. In simple terms, it is a set of routines, protocols, and tools for building software and applications.
Creating your own API allows you to expose the functionality of your application to other systems, and enables other developers to build new applications that interact with your existing system. With API, you can make your data and functionality available for others to consume and build on top of it.
API Design
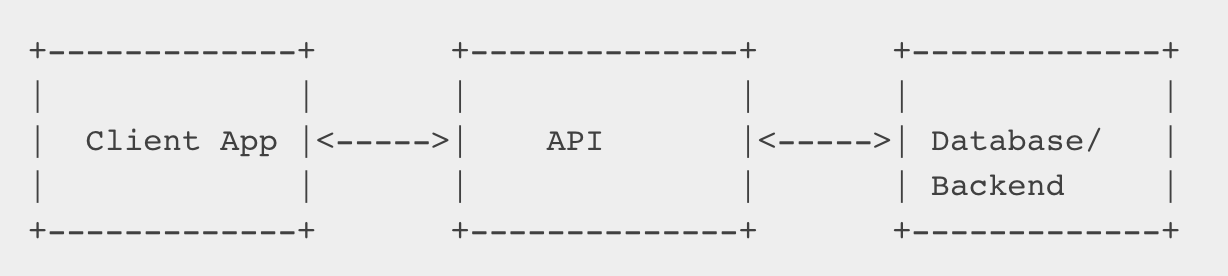
Here is a simple design diagram that illustrates the general architecture of an API:
In the diagram, the client app is the application that makes the API calls to the API server. The API server handles the requests from the client and interacts with the backend (database) or other services to retrieve or manipulate the data. The API server then returns the appropriate response to the client app.
It's important to note that the API server acts as an intermediary between the client app and the backend services, allowing for a separation of concerns and flexibility in the underlying implementation. This means that the client app can change or update without affecting the backend services and vice versa.
API development made easy
There are many different ways to build an API in Python, but one of the most popular and well-documented frameworks is Flask. Flask is a micro-framework that makes it easy to create web applications and APIs quickly.
To get started with Flask, you'll first need to install it by running the following command:
pip install FlaskThen, you can create a new Python file and import the Flask library. In this file, you will define the endpoint functions, in other words, the methods that should be executed when a specific endpoint is hit. Here is a basic example of how to create a simple endpoint that returns a "Hello, World!" message when the root path (/) is accessed:
from flask import Flask, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
return jsonify(message="Hello, World!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
In this example, the @app.route('/') decorator is used to define the endpoint, and the hello() function is executed when the endpoint is accessed. The jsonify function is used to format the response as a JSON object.
You can test your API by running the Python file and accessing the root path in your web browser, or using a tool such as curl or postman.
This is just the beginning of what you can do with Flask and creating an API, you can define different endpoints, use variables in the path, extract query parameters, handle post request
As you can see, creating an API can be simple and straightforward, and with the help of a framework like Flask, you can quickly build a robust and scalable API for your application.
We hope this example gives you a good starting point for building your own APIs with Flask. As always, thank you for reading and we look forward to providing you with more informative content in the future.